Cutaneous Loxoscelism: Patient with multiple bites and contraindication to sulfa drugs. Case report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17533/udea.iatreia.v31n1a08Keywords:
arachnid accident, cutaneous loxoscelism, hyperbaric chamber , loxoscelismoAbstract
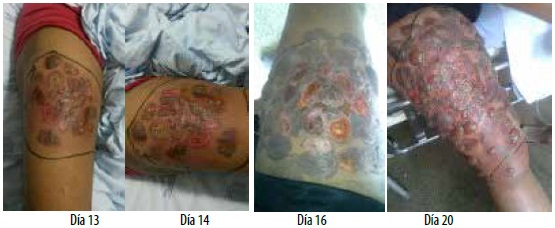
We report the case of a young adult patient who presented bites by Loxosceles spider and its hatchlings with a history of importance of such allergy anaphylaxis severe by sulfa drugs and NSAIDs, generalized anxiety disorder, who presented initial torpid with new lesions even 15 days after the accident and despite having used several pharmacological alternatives reported in the literature as useful (colchicine , antihistamines, steroids, blood thinners, antibiotics) had not been answered, to the use of oxygen for hyperbaric chamber with which brake the appearance of new and improved reepithelialization injury without surgery, with successful evolution.
Downloads
References
(1.) Gertsch WJ, Ennik F. The spider genus Loxoscelismo in North América, Central América and the West Indies (Araneae loxoscelidae). Bull Am Mus Nat Hist. 1983;175:264-360.
(2.) Swanson DL, Vetter RS. Loxoscelism. Clin Dermatol. 2006 May-Jun;24(3):213-21.
(3.) Van Den Berg CW, De Andrade RM, Magnoli FC, Marchbank KJ, Tambourgi DV. Loxoscelismo spider venom induces metalloproteinase mediated cleavage of MCP/CD46 and MHCI and induces protection against C-mediated lysis. Immunology. 2002 Sep;107(1):102-10.
(4.) Southcott RV. Spiders of the genus Loxoscelismo in Australia. Med J Aust. 1976 Mar;1(12):406-8.
(5.) Quintana Castillo JC, Otero Patiño R. Envenenamiento aracnídico en las Américas. Medunab. 2002;5(13):14-22.
(6.) Otero R. Envenenamiento por mordeduras de arañas y ciempiés. En: Otero, R, Ángel R, García M. Primer Simposio Colombiano de Toxinología. Medellín: Ecográficas; 1998. p. 179-88.
(7.) Hogan CJ, Barbaro KC, Winkel K. Loxoscelism: old obstacles, new directions. Ann Emerg Med. 2004 Dec;44(6):608-24.
(8.) Swanson DL, Vetter RS. Bites of brown recluse spiders and suspected necrotic arachnidism. N Engl J Med. 2005 Feb;352(7):700-7.
(9.) Young AR, Pincus SJ. Comparison of enzymatic activity from three species of necrotising arachnids in Australia: Loxoscelismo rufescens, Badumna insignis and Lampona cylindrata. Toxicon. 2001 Feb-Mar;39(2-3):391-400.
(10.) Schenone H. Cuadros tóxicos producidos por mordeduras de araña en Chile: latrodectismo y loxoscelismo. Rev Méd Chile. 2003 Abr; 131: 437-44. DOI 10.4067/S0034-98872003000400013.
(11.) Schenone H. [Cutaneous loxoscelism with edematous predominance]. Bol Chil Parasitol. 1998 Jul-Dec;53(3-4):78-83. Spanish.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2018 Universidad de Antioquia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Papers published in the journal are available for use under the Creative Commons license, specifically Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International.
The papers must be unpublished and sent exclusively to the Journal Iatreia; the author uploading the contribution is required to submit two fully completed formats: article submission and authorship responsibility.