Fast Skeletal Muscle Troponin and Tropomyosin as a Dietary Source of Antidiabetic and Antihypertensive Bioactive Peptides: An In Silico Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17533/udea.vitae.v30n1a347310Keywords:
Bioactive peptides, Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitors, Tropomyosin, TroponinAbstract
Background: The nutraceutical properties of food hydrolysates rely on multiple biochemical interactions involving the modulation of enzymes and cellular receptors. Numerous bioactive peptides released from troponin and tropomyosin digestion have been identified. Their characterization has mostly been performed by hydrolysis catalyzed by proteases unrelated to the human digestive system.
Objective: This study aimed to determine the bioactive profile of beef, pork, and chicken meat by analyzing the frequency and pharmacokinetics of biopeptides released from troponin and tropomyosin.
Methods: In silico digestion and biopeptide release frequency were studied by three parameters; bioactive fragments release frequency (AE), frequency percentage (W), and mean occurrence (AS), all stated on the BIOPEP-UWM platform. Further on, hydrolysis end-products were screened based on gastrointestinal-absorption probability and pharmacokinetic profiling performed on SwissADME, SwissTargetPrediction, and ADME/Tlab bioinformatics web tools. Statistical analyses were performed using a one-way ANOVA test.
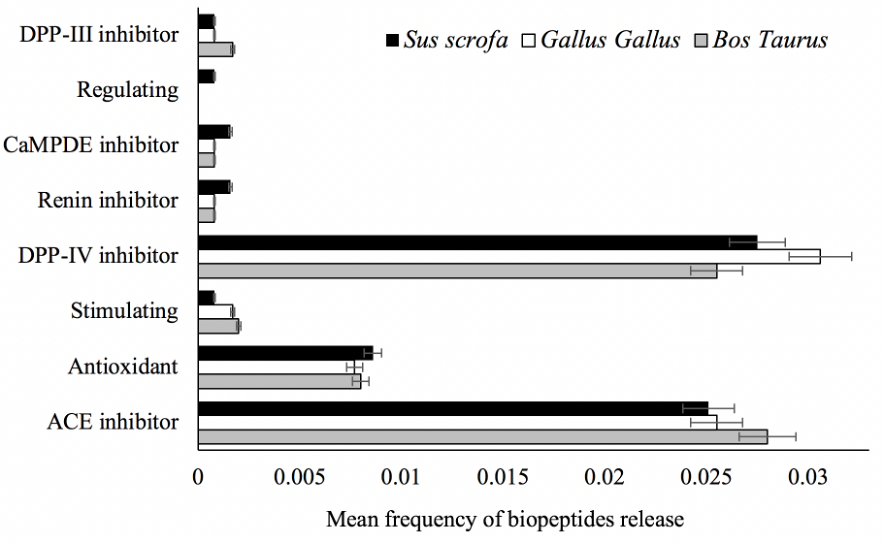
Results: Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibiting biopeptides exhibited the highest release frequency. Moreover, W and AS parameters showed no significant difference (p>0.05) between the myofibrillar isoforms assessed. Seven biopeptides were classified as highly absorbable and reported optimal drug-likeness compliance. Although biopeptides hold good pharmacokinetic properties, the therapeutic potency of biopeptides has been shown to be lower than those of DPP-IV and ACE-inhibiting drugs.
Conclusions: Troponin and tropomyosin are rich dietary sources of bioactive peptides, mainly DPP-IV and ACE inhibitors. Digestion end-products are mainly dipeptides with optimal pharmacokinetic and drug-like properties, suggesting a potential therapeutic application in hypertensive and hyperglycemic disorders.
Downloads
References
Ahmad RS, Imran A, Hussain MB. Nutritional Composition of Meat. In: Arshad MS, editor. Meat Science and Nutrition [Internet]. InTech; 2018 [cited 2021 Jun 16]. Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/meat-science-and-nutrition/nutritional-composition-of-meat
Badui S. Química De Los Alimentos. [Internet]. Pearson Educación de México, SA de CV; 2006 [cited 2021 Jun 16]. Available from: https://public.ebookcentral.proquest.com/choice/publicfullrecord.aspx?p=5133798
Premi, M., Bansal, V. Nutraceuticals for Management of Metabolic Disorders. In: Treating endocrine and metabolic disorders with herbal medicines. 2021. p. 298–320.
Xing L, Liu R, Cao S, Zhang W, Guanghong Z. Meat protein based bioactive peptides and their potential functional activity: a review. Int J Food Sci Technol. 2019;54(6):1956–66. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.14132
Iwaniak A, Minkiewicz P, Pliszka M, Mogut D, Darewicz M. Characteristics of Biopeptides Released In Silico from Collagens Using Quantitative Parameters. Foods. 2020;9(7):965. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9070965
Wang TY, Hsieh CH, Hung CC, Jao CL, Lin PY, Hsieh YL, et al. A study to evaluate the potential of an in silico approach for predicting dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory activity in vitro of protein hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2017;234:431–8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.05.035
Jao C-L, Hung C-C, Tung Y-S, Lin P-Y, Chen M-C, Hsu K-C. The development of bioactive peptides from dietary proteins as a dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the management of type 2 diabetes. BioMedicine. 2015;5(3):14. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7603/s40681-015-0014-9
Acquah C, Dzuvor CKO, Tosh S, Agyei D. Anti-diabetic effects of bioactive peptides: recent advances and clinical implications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;1–14. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1851168
Tu M, Cheng S, Lu W, Du M. Advancement and prospects of bioinformatics analysis for studying bioactive peptides from food-derived protein: Sequence, structure, and functions. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2018;105:7–17. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.04.005
Dong J, Wang N-N, Yao Z-J, Zhang L, Cheng Y, Ouyang D, et al. ADMETlab: a platform for systematic ADMET evaluation based on a comprehensively collected ADMET database. J Cheminformatics. 2018;10(1):29. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13321-018-0283-x
Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V. SwissTargetPrediction: updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(W1):W357–64. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz382
The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: a worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D506–15. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1049
Minkiewicz, Iwaniak, Darewicz. BIOPEP-UWM Database of Bioactive Peptides: Current Opportunities. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):5978. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235978
Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V. SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):42717. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42717
Lee Y-S, Jun H-S. Anti-diabetic actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 on pancreatic beta-cells. Metabolism. 2014;63(1):9–19. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2013.09.010
Casanova-Martí À, Bravo FI, Serrano J, Ardévol A, Pinent M, Muguerza B. Antihyperglycemic effect of a chicken feet hydrolysate via the incretin system: DPP-IV-inhibitory activity and GLP-1 release stimulation. Food Funct. 2019;10(7):4062–70. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO00695H
Soler MJ, Batlle D. Revisiting the renin-angiotensin system. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021;529:111268. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2021.111268
Martin M, Deussen A. Effects of natural peptides from food proteins on angiotensin converting enzyme activity and hypertension. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(8):1264–83. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2017.1402750
Suetsuna K, Ukeda H, Ochi H. Isolation and characterization of free radical scavenging activities peptides derived from casein. J Nutr Biochem. 2000;11(3):128–31. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0955-2863(99)00083-2
Liu C, Ren D, Li J, Fang L, Wang J, Liu J, et al. Cytoprotective effect and purification of novel antioxidant peptides from hazelnut (C. heterophylla Fisch) protein hydrolysates. J Funct Foods. 2018;42:203–15. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2017.12.003
Deniau B, Rehfeld L, Santos K, Dienelt A, Azibani F, Sadoune M, et al. Circulating dipeptidyl peptidase 3 is a myocardial depressant factor: dipeptidyl peptidase 3 inhibition rapidly and sustainably improves haemodynamics. Eur J Heart Fail. 2020;22(2):290–9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ejhf.1601
Morifuji M, Koga J, Kawanaka K, Higuchi M. Branched-Chain Amino Acid-Containing Dipeptides, Identified from Whey Protein Hydrolysates, Stimulate Glucose Uptake Rate in L6 Myotubes and Isolated Skeletal Muscles. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2009;55(1):81–6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3177/jnsv.55.81
Goraya TA, Cooper DMF. Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase (PDE1): Current perspectives. Cell Signal. 2005;17(7):789–97. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2004.12.017
O’Brien JJ, O’Callaghan JP, Miller DB, Chalgeri S, Wennogle LP, Davis RE, et al. Inhibition of calcium-calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase (PDE1) suppresses inflammatory responses. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2020;102:103449. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2019.103449
Ramya K, Suresh R, Kumar HY, Kumar BRP, Murthy NBS. Decades-old renin inhibitors are still struggling to find a niche in antihypertensive therapy. A fleeting look at the old and the promising new molecules. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020;28(10):115466. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115466
Ignat’ev DA, Vorob’ev VV, Ziganshin RKh. Effects of a number of short peptides isolated from the brain of the hibernating ground squirrel on the eeg and behavior in rats. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 1998;28(2):158–66. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02461962
Martini S, Conte A, Tagliazucchi D. Comparative peptidomic profile and bioactivities of cooked beef, pork, chicken and turkey meat after in vitro gastro-intestinal digestion. J Proteomics. 2019;208:103500. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2019.103500
Mora L, Gallego M, Toldrá F. ACEI-Inhibitory Peptides Naturally Generated in Meat and Meat Products and Their Health Relevance. Nutrients. 2018;10(9):1259. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091259
Lan VTT, Ito K, Ohno M, Motoyama T, Ito S, Kawarasaki Y. Analyzing a dipeptide library to identify human dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor. Food Chem. 2015;175:66–73. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.11.131
Nongonierma AB, Mooney C, Shields DC, FitzGerald RJ. Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV and xanthine oxidase by amino acids and dipeptides. Food Chem. 2013;141(1):644–53. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.02.115
Byun H-G, Kim S-K. Structure and Activity of Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Alaskan Pollack Skin. BMB Rep. 2002;35(2):239–43. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5483/BMBRep.2002.35.2.239
Cheung, H. S., Wang, F. L., Ondetti, M. A., Sabo, E. F., Cushman, D. W. Binding of peptide substrates and inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Importance of the COOH-terminal dipeptide sequence. J Biol Chem [Internet]. 1980;255(2). Available from: https://doi.org/pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6243277/
Wu H, He H-L, Chen X-L, Sun C-Y, Zhang Y-Z, Zhou B-C. Purification and identification of novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from shark meat hydrolysate. Process Biochem. 2008;43(4):457–61. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2008.01.018
Ryan JT, Ross RP, Bolton D, Fitzgerald GF, Stanton C. Bioactive Peptides from Muscle Sources: Meat and Fish. Nutrients. 2011;3(9):765–91. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu3090765
Keller F, Hartmann B, Czock D. Time of effect duration and administration interval for sitagliptin in patients with kidney failure. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2014;39(2):77–85. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-013-0164-7
Lin Y, Feng M, Lu C-W, Lei Y-P, He Z-M, Xiong Y. Preservation of vascular DDAH activity contributes to the protection of captopril against endothelial dysfunction in hyperlipidemic rabbits. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;798:43–8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.01.041
Doroschuk VO, Makukha OG. The peculiarities of the interphase distribution of amino acids in the cloud point extraction systems. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Asp. 2017;520:757–63. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.02.036
Das T, Mehta CH, Nayak UY. Multiple approaches for achieving drug solubility: an in silico perspective. Drug Discov Today. 2020;25(7):1206–12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2020.04.016
Acquah C, Stefano ED, Udenigwe CC. Role of hydrophobicity in food peptide functionality and bioactivity. J Food Bioact. 2018;4(1):88–98. DOI: https://doi.org/10.31665/JFB.2018.4164
Yosipof A, Guedes RC, García-Sosa AT. Data Mining and Machine Learning Models for Predicting Drug Likeness and Their Disease or Organ Category. Front Chem. 2018;6:162. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2018.00162
Tian S, Li Y, Wang J, Zhang J, Hou T. ADME Evaluation in Drug Discovery. 9. Prediction of Oral Bioavailability in Humans Based on Molecular Properties and Structural Fingerprints. Mol Pharm. 2011;8(3):841–51. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/mp100444g
Isvoran A, Louet M, Vladoiu DL, Craciun D, Loriot M-A, Villoutreix BO, et al. Pharmacogenomics of the cytochrome P450 2C family: impacts of amino acid variations on drug metabolism. Drug Discov Today. 2017;22(2):366–76. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2016.09.015
Smith DA, Beaumont K, Maurer TS, Di L. Relevance of Half-Life in Drug Design. J Med Chem. 2018;61(10):4273–82. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00969
Iwaniak A, Minkiewicz P, Darewicz M, Hrynkiewicz M. Food protein-originating peptides as tastants - Physiological, technological, sensory, and bioinformatic approaches. Food Res Int. 2016;89:27–38. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2016.08.010
Bayes-Genis A, Barallat J, Richards AM. A Test in Context: Neprilysin. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68(6):639–53. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2016.04.060
Salazar J, Rojas-Quintero J, Cano C, Pérez JL, Ramírez P, Carrasquero R, et al. Neprilysin: A Potential Therapeutic Target of Arterial Hypertension? Curr Cardiol Rev. 2020;16(1):25–35. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2174/1573403X15666190625160352
Cui J, Jia J. Natural COX-2 Inhibitors as Promising Anti-inflammatory Agents: An Update. Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(18):3622–46. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867327999200917150939
Reyes-Díaz A, Del-Toro-Sánchez CL, Rodríguez-Figueroa JC, Valdéz-Hurtado S, Wong-Corral FJ, Borboa-Flores J, et al. Legume Proteins as a Promising Source of Anti-Inflammatory Peptides. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2019;20(12):1204–17. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203720666190430110647
Lim WC, Khan AM. Mapping HLA-A2, -A3 and -B7 supertype-restricted T-cell epitopes in the ebolavirus proteome. BMC Genomics. 2018;19(S1):42. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-4328-8
Herrera‐Ruiz D, Knipp GT. Current Perspectives on Established and Putative Mammalian Oligopeptide Transporters. J Pharm Sci. 2003;92(4):691–714. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.10303
Wan T, Li X, Sun Y-M, Li Y-B, Su Y. Role of the calpain on the development of diabetes mellitus and its chronic complications. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015;74:187–90. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2015.08.008
Yang. Increased expression of calpain and elevated activity of calcineurin in the myocardium of patients with congestive heart failure. Int J Mol Med [Internet]. 2010 May 25 [cited 2021 Jun 11];26(1). Available from: http://www.spandidos-publications.com/ijmm/26/1/159
Covington MD, Schnellmann RG. Chronic high glucose downregulates mitochondrial calpain 10 and contributes to renal cell death and diabetes-induced renal injury. Kidney Int. 2012;81(4):391–400. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2011.356
Dókus LE, Yousef M, Bánóczi Z. Modulators of calpain activity: inhibitors and activators as potential drugs. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2020;15(4):471–86. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/17460441.2020.1722638
Donkor IO. An update on the therapeutic potential of calpain inhibitors: a patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2020;30(9):659–75. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/13543776.2020.1797678
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Jorge Andrés Barrero, María Alejandra Barrero, Angélica María González Clavijo, Claudia Marcela Cruz

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Copyright Notice and Open Access Statement
The Journal Vitae works under the Open Access license, and the published manuscripts remain available for the public, both on the Journal's website and in databases, under the Creative Commons license, "Noncommercial Attribution" and "Share alike" systems, adopted in Colombia. Hence, when the authors agree to publish in the Journal Vitae, they will not have the right to economic retributions on publications and reproductions through different diffusion media. The documents are freely available to the internet public, permitting users to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts and pass them as data to software. The only constraint on reproduction and distribution, should be to give authors control over the integrity of their work and the right to be appropriately acknowledged and cited.
Authors declare that:
-
They are the intellectual property owners and are responsible for all the information stated in the article.
-
This manuscript has not been submitted or published in other printed or digital media. They accept the responsibility for the judgments, opinions, and points of view expressed in the published article and, therefore, they exonerate Universidad de Antioquia and Journal Vitae from any process.
-
They exempt Universidad de Antioquia and Journal Vitae from settling conflicts or disputes related to the authorship of the referred article.
-
They accept the revision of the original manuscript by suitable personnel, and they bind themselves to perform the corrections appointed or suggested by the assessors.
-
Therefore, they know the editorial process and will not bind the Editorial Board of the Journal to assume any obligations regarding the volume and issue in which the article is published.
-
They transfer the rights of publication, reprinting, and distribution of the article from the moment of its approval, in print and digital format, without the right to economic rewards, and under the licensing conditions considered relevant by Journal Vitae.
-
They fully authorize Universidad de Antioquia and Journal Vitae to submit the published material to the diverse databases and indexing systems where the Journal can be found to comply with the requirements of the regulatory authorities to maintain the national classification of journals.
-
They will assume the article publication costs established for the current issue, and they will make the payment as soon as they are informed about the volume and the issue in which the final version of the article is published.
-
After the article is published, you can share digital or printed copies in a noncommercial manner. You will be able to use the paper in your institution or company for educational or research purposes, including the use in course programs.
Conflict of interest: Authors are responsible for recognizing and disclosing any financial or other benefits that could be perceived to bias their work, acknowledging all financial support and any personal connections with potential sponsors. Examples of such conflicts include receiving research funds or honoraria, serving on advisory boards, stock ownership, or employment and consulting arrangements. Authors without such connections should clearly state that they have no financial support or personal relationships that could be perceived to bias their work. All conflicts of interest should be disclosed on the author's identification page of the manuscript.









